
You do not need to cast input data as a Raster object when using operators.You do not need to put the output raster name or the equal sign ( =) in the expression, since the output name is specified in the Output raster parameter.The Map Algebra syntax used in this tool is the same, with the following exceptions: Not only can you access Map Algebra from the Raster Calculator tool, but you can also access it in Python scripting using the Spatial Analyst ArcPy module. If these rules are not adhered to, the expression may be invalid and will not execute, or you may get results you did not expect. The Map Algebra used in Raster Calculator has a syntax, or a set of rules, that must be followed to create a valid expression. Map Algebra is a simple and powerful algebra with which you canĮxecute all Spatial Analyst tools, operators, and functions to See the section below to learn more about the syntax rules for Map Algebra. The expression must be entered with valid syntax. The expression is the Map Algebra expression to be run. When you select these symbols, that operator is entered in the expression where the pointer is currently positioned.

The operators in the list allow you to enter mathematical (addition, division, and so on) and logical (greater than, equal to, and so on) operators in the expression. A tool can be placed anywhere in the expression, but it should be placed in a position that produces valid Map Algebra syntax. The remaining input required by the tool must then be entered. When you click a tool in the list, the tool name and open and close parentheses () are placed in the expression where the pointer is currently positioned. The Tools list is a selection of tools that can be used in the Map Algebra expression. When the tool is used in ModelBuilder, the raster list also contains Raster model variables. The raster list contains the layers in the contents and datasets added with the Add raster button. The input Rasters list identifies the input that can be used in the Map Algebra expression. There are three main areas on the tool dialog box that are used to create a Map Algebra expression: Rasters, Tools, and the expression box. When multiple tools or operators are used in one expression, the performance of this equation will generally be faster than executing each of the operators or tools individually. Raster Calculator is designed to execute a single-line algebraic expression using multiple tools and operators.
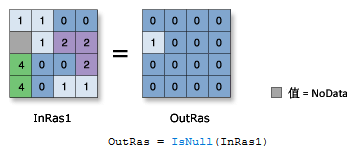
#Arcmap raster calculator con pick setnull how to#
If you don't have Spatial Analyst you can try the QGIS raster calculator, which is very much like Esri Raster Calculator or GDAL_Calc, both will work if you're prepared to learn how to use them.The Raster Calculator tool is not intended to be used in scripting environments and is not available in the standard Spatial Analyst ArcPy module. With both of these tools the output will be the same as the input, so if input is Float 32 then output will also be Float 32. Will give you a raster that is NoData for less than 215 and the value of the input for values greater than 215.

For example to extract only a range:Ĭon is a bit more powerful when used in raster calculator, you can use it to set null values or replace values with a constant (or a different raster):

The biggest problem is creating an appropriate 'where clause'. Your friends in ArcGis are Con and Extract by Attributes, this will allow you to specify a clause on what values you want to keep, anything else will be Null.įor example, if you wanted only the parts of a DEM that are above 0: You will need the Spatial Analyst extension to perform this type of extraction. Seeing as you talk about SetNull I will assume ArcGis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
